This notebook demonstrates how to access Google Cloud CMIP6 data using intake-esm.
Intake-esm is a data cataloging utility built on top of intake, pandas, and xarray. Intake-esm aims to facilitate:
- the discovery of earth’s climate and weather datasets.
- the ingestion of these datasets into xarray dataset containers.
Imports¶
It’s basic usage is shown below. To begin, let’s import intake:
import intakeLoad the Catalog¶
At import time, intake-esm plugin is available in intake’s registry as
esm_datastore and can be accessed with intake.open_esm_datastore() function.
Use the intake_esm.tutorial.get_url() method to access smaller subsetted catalogs for tutorial purposes.
import intake_esm
url = intake_esm.tutorial.get_url('google_cmip6')
print(url)
cat = intake.open_esm_datastore(url)
catThe summary above tells us that this catalog contains 261 data assets. We can get more information on the individual data assets contained in the catalog by looking at the underlying dataframe created when we load the catalog:
cat.df.head()The first data asset listed in the catalog contains:
the Northward Wind (variable_id=‘va’), as a function of latitude, longitude, time,
the latest version of the IPSL climate model (source_id=‘IPSL-CM6A-LR’),
hindcasts initialized from observations with historical forcing (experiment_id=‘historical’),
developed by theInstitut Pierre Simon Laplace (instution_id=‘IPSL’),
run as part of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (activity_id=‘CMIP’)
And is located in Google Cloud Storage at ‘gs://cmip6/CMIP6/CMIP/IPSL/IPSL-CM6A-LR/historical/r2i1p1f1/Amon/va/gr/v20180803/’.
Finding unique entries¶
To get unique values for given columns in the catalog, intake-esm provides a ~intake_esm.core.esm_datastore.unique method:
Let’s query the data catalog to see what models(source_id), experiments
(experiment_id) and temporal frequencies (table_id) are available.
unique = cat.unique()
uniqueactivity_id [CMIP]
institution_id [IPSL, CCCma]
source_id [IPSL-CM6A-LR, CanESM5]
experiment_id [historical]
member_id [r2i1p1f1, r8i1p1f1, r30i1p1f1, r29i1p1f1, r3i...
table_id [Amon, Oyr]
variable_id [va, ua, o2]
grid_label [gr, gn]
zstore [gs://cmip6/CMIP6/CMIP/IPSL/IPSL-CM6A-LR/histo...
dcpp_init_year []
version [20180803, 20190429, 20190802, 20191204]
derived_variable_id []
dtype: objectunique['source_id']['IPSL-CM6A-LR', 'CanESM5']unique['experiment_id']['historical']unique['table_id']['Amon', 'Oyr']Search for specific datasets¶
The ~intake_esm.core.esm_datastore.search method allows the user to perform a query on a catalog using keyword arguments. The keyword argument names must match column names in the catalog. The search method returns a subset of the catalog with all the entries that match the provided query.
In the example below, we are are going to search for the following:
- variable_d:
o2which stands formole_concentration_of_dissolved_molecular_oxygen_in_sea_water - experiments: [‘historical’, ‘ssp585’]:
- historical: all forcing of the recent past.
- ssp585: emission-driven RCP8.5 based on SSP5.
- table_id:
0yrwhich stands for annual mean variables on the ocean grid. - grid_label:
gnwhich stands for data reported on a model’s native grid.
For more details on the CMIP6 vocabulary, please check this website, and Core Controlled Vocabularies (CVs) for use in CMIP6 GitHub repository.
cat_subset = cat.search(
experiment_id=["historical", "ssp585"],
table_id="Oyr",
variable_id="o2",
grid_label="gn",
)
cat_subsetLoad datasets using to_dataset_dict()¶
Intake-esm implements convenience utilities for loading the query results into
higher level xarray datasets. The logic for merging/concatenating the query
results into higher level xarray datasets is provided in the input JSON file and
is available under .aggregation_info property of the catalog:
cat.esmcat.aggregation_controlAggregationControl(variable_column_name='variable_id', groupby_attrs=['activity_id', 'institution_id', 'source_id', 'experiment_id', 'table_id', 'grid_label'], aggregations=[Aggregation(type=<AggregationType.union: 'union'>, attribute_name='variable_id', options={}), Aggregation(type=<AggregationType.join_new: 'join_new'>, attribute_name='member_id', options={'coords': 'minimal', 'compat': 'override'}), Aggregation(type=<AggregationType.join_new: 'join_new'>, attribute_name='dcpp_init_year', options={'coords': 'minimal', 'compat': 'override'})])To load data assets into xarray datasets, we need to use the ~intake_esm.core.esm_datastore.to_dataset_dict method. This method returns a dictionary of aggregate xarray datasets as the name hints.
dset_dict = cat_subset.to_dataset_dict(
xarray_open_kwargs={"consolidated": True, "decode_times": True, "use_cftime": True}
)[key for key in dset_dict.keys()]['CMIP.CCCma.CanESM5.historical.Oyr.gn',
'CMIP.IPSL.IPSL-CM6A-LR.historical.Oyr.gn']We can access a particular dataset as follows:
ds = dset_dict["CMIP.CCCma.CanESM5.historical.Oyr.gn"]
dsLet’s create a quick plot for a slice of the data:
ds.o2.isel(time=0,
lev=0,
member_id=range(1, 24, 4)
).plot(col="member_id", col_wrap=3, robust=True)<xarray.plot.facetgrid.FacetGrid at 0x163dd9210>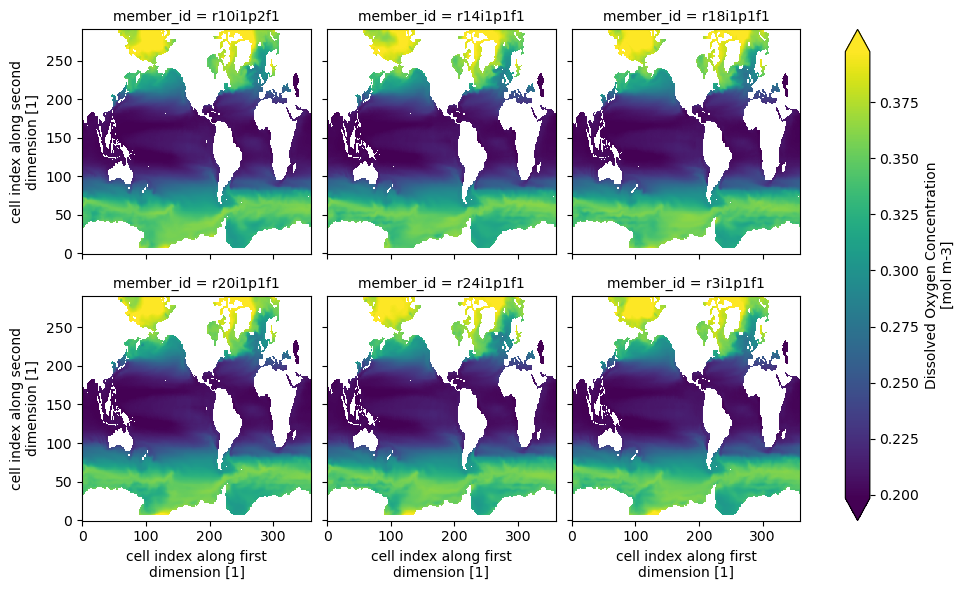
Use custom preprocessing functions¶
When comparing many models it is often necessary to preprocess (e.g. rename
certain variables) them before running some analysis step. The preprocess
argument lets the user pass a function, which is executed for each loaded asset
before combining datasets.
cat_pp = cat.search(
experiment_id=["historical"],
table_id="Oyr",
variable_id="o2",
grid_label="gn",
source_id=["IPSL-CM6A-LR", "CanESM5"],
member_id="r10i1p1f1",
)
cat_pp.dfdset_dict_raw = cat_pp.to_dataset_dict(xarray_open_kwargs={"consolidated": True})
for k, ds in dset_dict_raw.items():
print(f"dataset key={k}\n\tdimensions={sorted(list(ds.dims))}\n")Note that both models follow a different naming scheme. We can define a little
helper function and pass it to .to_dataset_dict() to fix this. For
demonstration purposes we will focus on the vertical level dimension which is
called lev in CanESM5 and olevel in IPSL-CM6A-LR.
def helper_func(ds):
"""Rename `olevel` dim to `lev`"""
ds = ds.copy()
# a short example
if "olevel" in ds.dims:
ds = ds.rename({"olevel": "lev"})
return dsdset_dict_fixed = cat_pp.to_dataset_dict(xarray_open_kwargs={"consolidated": True}, preprocess=helper_func)
for k, ds in dset_dict_fixed.items():
print(f"dataset key={k}\n\tdimensions={sorted(list(ds.dims))}\n")This was just an example for one dimension.
Check out xmip package for a full renaming function for all available CMIP6 models and some other utilities.